How to extend the service life of S9012?
First, ensure proper heat dissipation by using a heat sink or providing adequate airflow around the transistor. This helps prevent overheating and thermal stress. Second, avoid exceeding the maximum specified current and voltage ratings to prevent damage to the transistor. Use appropriate current-limiting resistors or voltage regulation circuits when interfacing with the transistor. Third, protect the transistor from electrostatic discharge (ESD) by using proper ESD precautions during handling and storage. Additionally, ensure a stable and clean power supply to prevent voltage spikes or fluctuations that may damage the transistor. Finally, avoid excessive mechanical stress or vibration that can cause physical damage to the transistor. By implementing these measures, the service life of the S9012 transistor can be extended, ensuring reliable and prolonged operation.
S9012 Uses
The S9012 is a widely used transistor belonging to the 9012 series of PNP bipolar junction transistors (BJTs). One of its main applications is as a switching transistor for low power electronic devices. Its ability to handle moderate current and voltage levels makes it suitable for controlling small loads, such as relays, LEDs, and small motors.
The S9012 is also commonly used in audio amplifier circuits, where it functions as a small signal amplifier. Its low noise and high gain characteristics are a great advantage for amplifying weak audio signals before input to power amplifiers or speakers. s9012 is also a key component for generating stable and accurate frequency signals in oscillator circuits.
In addition, due to its low power consumption and compact form factor, the S9012 is often used in portable electronic devices, including cell phones, tablets and digital cameras.
S9012 Equivalent Parts
There are several equivalents or replacements for the S9012 transistor that can be used in a variety of applications. The following are a few commonly used equivalents:
- 2N3906: It has similar electrical characteristics to the S9012 and can be used as a direct replacement in many circuits.
- BC327: It has comparable specifications to the S9012 and is typically used in audio and switching applications.
- MPSA92: It is suitable for low power applications and can replace the S9012 in a variety of circuits.
- C9012: The C9012 has similar characteristics to the S9012. It can be used as an equivalent component in many applications.
Проверка работоспособности КТ315
Иногда КТ315 может быть нерабочим из-за пробитого или закороченного перехода, поэтому перед использованием стоит проверить его np-переходы мультиметром. Отрицательный щуп прикрепляется к базе, а положительный — на выбор (коллектор или эмиттер). Если диоды исправны, то их значения должны быть не близки нулю, а также отсутствие пищания мультиметра.
Проверка работоспособности КТ361
Поскольку эти транзисторы часто применяются вместе, то исправность КТ361 тоже нужно узнать
Очень важно запомнить, что КТ361 противоположен 315, из-за чего работа должна совершаться наоборот. Здесь отрицательный щуп прикрепляется к коллектору (или эмиттеру), а положительный — к базе
Показатели должны быть не близки к нулю, мультиметр не должен сигнализировать (как и в предыдущем разделе).
S9012 Feature
The S9012 transistor is a general purpose PNP transistor with several distinguishing features:
1. High current capability: With a collector current of up to -0.5A, the S9012 transistor can handle large amounts of current for its size.
2. Low voltage operation: The transistor has a collector-emitter voltage of -40V and an emitter-base voltage of -5V.
3. Compact package: The S9012 is typically available in a small TO-92 package, making it suitable for space-sensitive applications.
4. Versatility: Its characteristics make it useful in a wide range of applications, including signal processing, power management, and switching applications.
5. High power dissipation: Despite its large size, the S9012 can dissipate a reasonable amount of power, with a total power dissipation of 625mW at 25°C.
6. Good gain characteristics: It has high DC current gain with hFE values between 64 and 300.
7. Low noise: The S9012 is known for its low noise operation, making it the best choice for audio amplification and similar applications.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the S9012 transistor proves to be a versatile and reliable component for various electronic applications. With its compact size and moderate current handling capabilities, it finds widespread use as a switching transistor, small-signal amplifier, and oscillator component. Its low cost and wide availability make it an economical choice for many projects. However, designers should be mindful of its limitations, such as lower power dissipation and limited frequency range. By considering these factors and implementing proper precautions, the S9012 transistor can effectively serve its intended purposes, contributing to the efficient functioning and longevity of electronic circuits.
Read More:
D882 Transistor Pinout, Equivalent, Uses and DatasheetWhat is Transistor hFE13003/MJE13003 Transistor: Pinout, Features, Equivalent and Uses2N6027 Transistor Datasheet, Pinout, Equivalent and UsesS9012 Transistor Datasheet, Pinout, Equivalent and Uses
S9012 Pinout
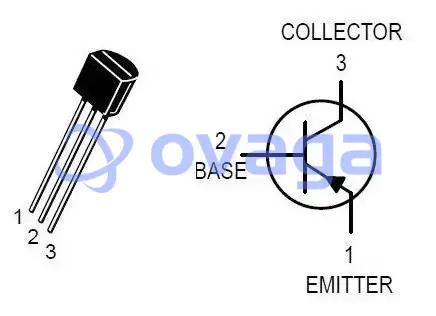
The S9012 transistor, typically found in a TO-92 package, has three pins. Here’s their configuration:
Emitter (E): The pin on the left when the flat surface of the package is facing you. In a PNP transistor like the S9012, the emitter releases carriers into the base.
Base (B): The central pin. The base controls the transistor’s operation by varying the current that passes through it.
Collector (C): The pin on the right when the flat surface of the package is facing you. For a PNP transistor like S9012, the collector collects the carriers from the emitter via the base.
Caution: Always remember to check the datasheet before using a transistor, as the pin configurations may vary depending on the manufacturer or specific variant of the transistor.
What is S9012 Transistor?
The S9012 is a general-purpose low-power PNP bipolar junction crystal manufactured by several companies including Fairchild Semiconductor and STMicroelectronics. It is typically packaged in TO-92 format and is therefore suitable for compact electronic circuits. It has a collector-emitter voltage (Vce) of -40 V, a collector current of -0.5A, and an emitter-base voltage (Vebo) of -5 V. Due to these characteristics, it is often used in amplifier stages and switching applications. It is ideal for signal processing, power management, and other low voltage applications, providing high current capability with minimal power consumption. Overall, the S9012 transistor is a versatile and reliable component in the electronics industry.
Pros and Cons of S9012 Transistor
The S9012 transistor offers a number of advantages in its application, but also has some limitations. Briefly, these advantages include its versatility, compact size, and modest current and voltage handling capabilities. On the downside, the S9012 has relatively low power dissipation compared to other transistors and a limited frequency range.
Pros
A key advantage of the S9012 transistor is its versatility. It is used in a wide variety of electronic circuits as a switching transistor, small signal amplifier, and oscillator element. This flexibility allows it to be used in a wide range of devices and systems. Another advantage is its compact size, which makes it suitable for integration into compact electronic devices and PCB designs where space is limited.
The S9012’s modest current and voltage handling capabilities facilitate control of small loads and amplification of weak signals. It can handle collector currents of up to 500mA and collector-emitter voltages of -25V, enabling it to switch and amplify signals in low power applications. In addition, the relatively low cost of the S9012 transistor saves money for many electronics projects and designs.
Cons
However, the S9012 transistor also has some limitations. One drawback is its lower power dissipation rating of 625 mW. This limits its use in high power applications that require transistors with higher power handling capabilities. In addition, the S9012 has a limited frequency range of up to 150 MHz. this is not suitable for applications that require higher frequency operation or faster switching speeds.
S9012 Specifications
Here are the specifications of the S9012 transistor:
| Specification | Value |
| Product Type | PNP Epitaxial Silicon Transistor |
| Collector-Base Voltage (VCBO) | -40V |
| Collector-Emitter Voltage (VCEO) | -25V |
| Emitter-Base Voltage (VEBO) | -5V |
| Collector Current (IC) | -500mA |
| Collector Power Dissipation (PC) | 625mW |
| Junction Temperature (Tj) | 150°C |
| Storage Temperature (Tstg) | -55 to 150°C |
| DC Current Gain (hFE) | 64 to 300 |
| Transition Frequency (fT) | 150 MHz |
| Package Type | TO-92 |
| Base-Emitter Saturation Voltage (VBE(sat)) | -0.85V |
| Base-Emitter On Voltage (VBE(on)) | -0.6V |
| Current Gain Bandwidth Product (fT) | 150MHz |
| Collector-Cutoff Current (ICEO) | -0.1μA |
| Emitter-Cutoff Current (IEBO) | -50nA |
| Fall Time (tf) | 250ns |
| Rise Time (tr) | 35ns |
| Storage Time (ts) | 2.5μs |
Аналоги КТ315
У транзистора имеется как отечественная замена, так и заграничная. Начнем с первой. Это КТ3102 (ТО-92). Он тоже кремниевый, с npn структурой, но с большей температурой (до +150 С), другим расположением диодов и более высокими электрическими возможностями. Можно сказать, что они, относительно, одинаковы.
Иностранные заменители: ВС547 (npn, высокочастотный (примерно в 300 МГц, когда у КТ315 — 250 МГц), расположение диодов как у КТ3102, температура до +150 С), PN2222 (300 МГц, цоколевка соответствует предыдущей, остальные характеристики примерно одинаковы с КТ315), 2SC9014 (температура от -55 С до +150 С, 270 МГц). Раньше зарубежные транзисторы выходили с корпусом КТ-13, но на данный момент таких уже не существует.
In Stock: 7949
United States
China
Canada
Japan
Russia
Germany
United Kingdom
Singapore
Italy
Hong Kong(China)
Taiwan(China)
France
Korea
Mexico
Netherlands
Malaysia
Austria
Spain
Switzerland
Poland
Thailand
Vietnam
India
United Arab Emirates
Afghanistan
Åland Islands
Albania
Algeria
American Samoa
Andorra
Angola
Anguilla
Antigua & Barbuda
Argentina
Armenia
Aruba
Australia
Azerbaijan
Bahamas
Bahrain
Bangladesh
Barbados
Belarus
Belgium
Belize
Benin
Bermuda
Bhutan
Bolivia
Bonaire, Sint Eustatius and Saba
Bosnia & Herzegovina
Botswana
Brazil
British Indian Ocean Territory
British Virgin Islands
Brunei
Bulgaria
Burkina Faso
Burundi
Cabo Verde
Cambodia
Cameroon
Cayman Islands
Central African Republic
Chad
Chile
Christmas Island
Cocos (Keeling) Islands
Colombia
Comoros
Congo
Congo (DRC)
Cook Islands
Costa Rica
Côte d’Ivoire
Croatia
Cuba
Curaçao
Cyprus
Czechia
Denmark
Djibouti
Dominica
Dominican Republic
Ecuador
Egypt
El Salvador
Equatorial Guinea
Eritrea
Estonia
Eswatini
Ethiopia
Falkland Islands
Faroe Islands
Fiji
Finland
French Guiana
French Polynesia
Gabon
Gambia
Georgia
Ghana
Gibraltar
Greece
Greenland
Grenada
Guadeloupe
Guam
Guatemala
Guernsey
Guinea
Guinea-Bissau
Guyana
Haiti
Honduras
Hungary
Iceland
Indonesia
Iran
Iraq
Ireland
Isle of Man
Israel
Jamaica
Jersey
Jordan
Kazakhstan
Kenya
Kiribati
Kosovo
Kuwait
Kyrgyzstan
Laos
Latvia
Lebanon
Lesotho
Liberia
Libya
Liechtenstein
Lithuania
Luxembourg
Macao(China)
Madagascar
Malawi
Maldives
Mali
Malta
Marshall Islands
Martinique
Mauritania
Mauritius
Mayotte
Micronesia
Moldova
Monaco
Mongolia
Montenegro
Montserrat
Morocco
Mozambique
Myanmar
Namibia
Nauru
Nepal
New Caledonia
New Zealand
Nicaragua
Niger
Nigeria
Niue
Norfolk Island
North Korea
North Macedonia
Northern Mariana Islands
Norway
Oman
Pakistan
Palau
Palestinian Authority
Panama
Papua New Guinea
Paraguay
Peru
Philippines
Pitcairn Islands
Portugal
Puerto Rico
Qatar
Réunion
Romania
Rwanda
Samoa
San Marino
São Tomé & Príncipe
Saudi Arabia
Senegal
Serbia
Seychelles
Sierra Leone
Sint Maarten
Slovakia
Slovenia
Solomon Islands
Somalia
South Africa
South Sudan
Sri Lanka
St Helena, Ascension, Tristan da Cunha
St. Barthélemy
St. Kitts & Nevis
St. Lucia
St. Martin
St. Pierre & Miquelon
St. Vincent & Grenadines
Sudan
Suriname
Svalbard & Jan Mayen
Sweden
Syria
Tajikistan
Tanzania
Timor-Leste
Togo
Tokelau
Tonga
Trinidad & Tobago
Tunisia
Turkey
Turkmenistan
Turks & Caicos Islands
Tuvalu
U.S. Outlying Islands
U.S. Virgin Islands
Uganda
Ukraine
Uruguay
Uzbekistan
Vanuatu
Vatican City
Venezuela
Wallis & Futuna
Yemen
Zambia
Zimbabwe
Quantity
Quick RFQ
S9012 Manufacturer
The S9012 transistor is manufactured by various semiconductor companies. Some well-known manufacturers that produce the S9012 transistor include:
1. Fairchild Semiconductor: Fairchild Semiconductor, now a part of ON Semiconductor, is a renowned semiconductor manufacturer that produces a wide range of electronic components, including transistors. They have been known to produce the S9012 transistor.
2. NXP Semiconductors: NXP Semiconductors is a leading global semiconductor company that specializes in the production of high-performance mixed-signal and standard semiconductor components. They also manufacture the S9012 transistor.
3. STMicroelectronics: STMicroelectronics is a major semiconductor manufacturer known for its comprehensive range of electronic components. They are also known to produce the S9012 transistor.
4. Texas Instruments: Texas Instruments (TI) is a prominent semiconductor company that develops and manufactures a wide array of semiconductor devices. They are known for producing various types of transistors, including the S9012.
S9012 CAD Model
Symbol:

It consists of two concentric circles representing the emitter and the base, with an arrow on the emitter indicating the direction of conventional current flow (in a PNP transistor, it points inwards, towards the base). There is also a line extending from the base that represents the collector.
Footprint:
The footprint of the S9012 transistor in a CAD model will typically represent its physical package type, which is commonly the TO-92 package.
A TO-92 package has three leads (Emitter, Base, and Collector) in a row, with a half-circle or rectangular body above them. In a footprint, the leads are depicted as three circular or oval pads, arranged in a straight line. The spacing between these pads corresponds to the lead pitch of the physical component, which is typically 2.54mm (0.1 inch) for the TO-92 package.
3D Model:
The 3D CAD model of the S9012 transistor will reflect its actual physical attributes. It will typically depict the transistor in its commonly used TO-92 package.
In a TO-92 package, the transistor has a small, usually black or dark-colored, plastic body. This body is somewhat half-cylindrical or rectangular in shape, with a flat side and a rounded side. The flat side generally has the part number printed on it.
Emerging from the bottom of the plastic body, there are three metal leads (pins) arranged in a straight line. These represent the emitter, base, and collector of the transistor. The leads are usually slightly bent or formed to facilitate insertion into a printed circuit board (PCB).
Характеристики популярных аналогов
Наименование производителя: KT972A
- Тип материала: Si
- Полярность: NPN
- Максимальная рассеиваемая мощность (Pc): 8 W
- Макcимально допустимое напряжение коллектор-база (Ucb): 60 V
- Макcимально допустимое напряжение эмиттер-база (Ueb): 5 V
- Макcимальный постоянный ток коллектора (Ic): 4 A
- Предельная температура PN-перехода (Tj): 150 °C
- Граничная частота коэффициента передачи тока (ft): 200 MHz
- Статический коэффициент передачи тока (hfe): 750
Наименование производителя: WW263
- Тип материала: Si
- Полярность: NPN
- Максимальная рассеиваемая мощность (Pc): 65 W
- Макcимально допустимое напряжение коллектор-база (Ucb): 100 V
- Макcимально допустимое напряжение коллектор-эмиттер (Uce): 100 V
- Макcимально допустимое напряжение эмиттер-база (Ueb): 5 V
- Макcимальный постоянный ток коллектора (Ic): 10 A
- Предельная температура PN-перехода (Tj): 150 °C
- Ёмкость коллекторного перехода (Cc): 200 pf
- Статический коэффициент передачи тока (hfe): 1000
- Корпус транзистора: TO220
Наименование производителя: U2T833
- Тип материала: Si
- Полярность: NPN
- Максимальная рассеиваемая мощность (Pc): 60 W
- Макcимально допустимое напряжение коллектор-эмиттер (Uce): 300 V
- Макcимально допустимое напряжение эмиттер-база (Ueb): 12 V
- Макcимальный постоянный ток коллектора (Ic): 5 A
- Предельная температура PN-перехода (Tj): 200 °C
- Статический коэффициент передачи тока (hfe): 1000
- Аналоги (замена) для U2T833
Наименование производителя: U2T832
- Тип материала: Si
- Полярность: NPN
- Максимальная рассеиваемая мощность (Pc): 60 W
- Макcимально допустимое напряжение коллектор-эмиттер (Uce): 200 V
- Макcимально допустимое напряжение эмиттер-база (Ueb): 12 V
- Макcимальный постоянный ток коллектора (Ic): 5 A
- Предельная температура PN-перехода (Tj): 200 °C
- Статический коэффициент передачи тока (hfe): 1000
Наименование производителя: U2T823
- Тип материала: Si
- Полярность: NPN
- Максимальная рассеиваемая мощность (Pc): 35 W
- Макcимально допустимое напряжение коллектор-эмиттер (Uce): 300 V
- Макcимально допустимое напряжение эмиттер-база (Ueb): 12 V
- Макcимальный постоянный ток коллектора (Ic): 5 A
- Предельная температура PN-перехода (Tj): 200 °C
- Статический коэффициент передачи тока (hfe): 1000
Наименование производителя: U2T6O1
- Тип материала: Si
- Полярность: NPN
- Максимальная рассеиваемая мощность (Pc): 50 W
- Макcимально допустимое напряжение коллектор-база (Ucb): 80 V
- Макcимальный постоянный ток коллектора (Ic): 20 A
- Предельная температура PN-перехода (Tj): 200 °C
- Статический коэффициент передачи тока (hfe): 1000
- Корпус транзистора: TO66
Наименование производителя: U2T605
- Тип материала: Si
- Полярность: NPN
- Максимальная рассеиваемая мощность (Pc): 50 W
- Макcимально допустимое напряжение коллектор-база (Ucb): 150 V
- Макcимальный постоянный ток коллектора (Ic): 20 A
- Предельная температура PN-перехода (Tj): 200 °C
- Статический коэффициент передачи тока (hfe): 1000
- Корпус транзистора: TO66
Наименование производителя: TTD1415B
- Маркировка: D1415B
- Тип материала: Si
- Полярность: NPN
- Максимальная рассеиваемая мощность (Pc): 25 W
- Макcимально допустимое напряжение коллектор-база (Ucb): 120 V
- Макcимально допустимое напряжение коллектор-эмиттер (Uce): 100 V
- Макcимально допустимое напряжение эмиттер-база (Ueb): 6 V
- Макcимальный постоянный ток коллектора (Ic): 7 A
- Предельная температура PN-перехода (Tj): 150 °C
- Статический коэффициент передачи тока (hfe): 1000
- Корпус транзистора: TO220SIS
Мультивибратор на КТ315
Мультивибратор — это генератор широкой импульсной модуляции (или коротко ШИМ). Получается, что генератор будет выдавать сигнал либо постоянного плюса, либо постоянного минуса.
Принцип действий заключается в попеременном поступлении тока то к одному, то к другому светодиоду (их два). Частоту каждого из них можно менять (если резисторы будут разными, то и включение светодиодов тоже будет отличаться). Данная схема работает от напряжения 1,7 В до 16 В. Чтобы запустить схему понадобиться 3,2 В (этого будет достаточно, чтобы увидеть деятельность светодиодов).
Стоит отметить, что схема парная (2 конденсатора, 2 резистора, (2 RC-цепи), 2 светодиода), а вот значения транзисторов могут отличаться (от 220 Ом до 300 Ом), в таком случае схема все равно будет работать.
Надежная функциональность мультивибратора зависит от более высокого сопротивления одного из резисторов.
Отметим, что, чем больше сопротивление на переменном резисторе, тем больше будет мигать светодиод.