MJ3001 Transistor Equivalent Parts
The MJ3001 transistor is a specific part with its unique characteristics and specifications. However, there are some equivalent parts that can be used as substitutes in certain applications. Here are a few examples of MJ3001 transistor equivalents:
2N3055: The 2N3055 is a popular NPN transistor that can be used as an equivalent to the MJ3001 in many applications. It has similar power handling capabilities and voltage ratings.
MJ15003: The MJ15003 is another NPN transistor that can be used as a substitute for the MJ3001. It offers comparable power dissipation and current handling capabilities.
MJE3055: The MJE3055 is an NPN transistor that can be used as an alternative to the MJ3001 in some applications. It has a similar power rating and can handle moderate currents.
TIP3055: The TIP3055 is a high-power NPN transistor that can be used as a replacement for the MJ3001. It offers comparable power handling capabilities and voltage ratings.
MJ3001 Transistor Features
Here’s an extended table presenting the features of the MJ3001 transistor:
| Feature | Description |
| Transistor Type |
NPN (Negative-Positive-Negative) bipolar junction transistor |
| Maximum Collector Current (IC) | 10 Amperes |
| Maximum Collector-Base Voltage (VCBO) | 80 Volts |
| Maximum Collector-Emitter Voltage (VCEO) | 80 Volts |
| Maximum Emitter-Base Voltage (VEBO) | 5 Volts |
| Maximum Power Dissipation (Pd) | 150 Watts |
| Transition Frequency (ft) | 2 MHz |
| DC Current Gain (hFE) |
Typically ranging from 20 to 70 |
| Package Type |
TO-3 (Through-Hole Metal Can) |
| Operating Temperature Range | -65°C to +200°C |
| Junction Temperature (Tj) | #ERROR! |
| Storage Temperature Range | -65°C to +200°C |
| Mounting Style | Through-hole |
| Lead Material | Copper alloy |
| RoHS Compliance | Yes |
What is a MJ3001 Transistor?
The MJ3001 transistor is a high-power NPN (Negative-Positive-Negative) bipolar junction transistor. It is commonly used in electronic circuits for amplification and switching purposes. The transistor is designed to handle large currents and power dissipation, making it suitable for applications that require high power output. With a maximum collector current rating of 10 amperes, a voltage rating of 80 volts, and a power dissipation of 150 watts, the MJ3001 transistor is capable of delivering robust performance. Its durable construction and reliable characteristics make it a popular choice in various electronic devices and systems.
MJ3001 Transistor Uses
The MJ3001 transistor serves as a crucial component in power amplification applications. It finds common usage in audio power amplifiers and high-wattage audio systems. With its ability to handle high currents and power dissipation, the MJ3001 transistor can effectively drive speakers and deliver amplified signals with improved clarity and strength. Its robust performance in power amplification ensures the faithful reproduction of audio signals, making it suitable for use in professional audio equipment and high-quality sound systems.
Another significant application of the MJ3001 transistor lies in power switching circuits. Its capability to handle high currents makes it an ideal choice for controlling the flow of power in various devices such as motor drivers, solenoid drivers, and relays. By utilizing the MJ3001 transistor in power switching circuits, efficient and reliable control of electrical devices can be achieved. This is particularly useful in industrial automation systems, automotive applications, and other scenarios where precise control of power flow is necessary.
The MJ3001 transistor also plays a vital role in voltage regulation and power supply circuits. Its ability to handle high currents and power dissipation makes it suitable for maintaining stable voltage levels and delivering consistent power output. By incorporating the MJ3001 transistor in voltage regulator circuits, fluctuations in input voltage can be mitigated, ensuring a reliable and stable power supply for sensitive electronic devices. This makes it valuable in applications such as power supplies for computer systems, telecommunications equipment, and industrial control systems.
Overall, the MJ3001 transistor’s versatile applications in power amplification, power switching, and voltage regulation make it an indispensable component in a wide range of electronic systems. Its high-power capabilities, combined with reliable performance, ensure efficient power handling and control, enabling the reliable operation of various devices and systems.
MJ3001 Transistor Datasheet
The datasheet for the MJ3001 transistor provides a wealth of detailed technical information essential for understanding and utilizing this high-power NPN bipolar junction transistor. Within the datasheet, readers will find an in-depth exploration of the MJ3001 transistor’s electrical ratings, thermal data, pin configuration, and package dimensions. Additionally, the datasheet provides crucial insights into the transistor’s operating conditions, recommended biasing arrangements, and thermal management considerations.
Click to view the form:
For more information about Transistor, visit the article below:
Conclusion
In conclusion, this article provides a comprehensive exploration of the MJ3001 transistor, covering all aspects necessary to understand and utilize this versatile electronic component. This article provides a holistic view of the MJ3001 transistor, from pin configuration to equivalent replacements, datasheet analysis and practical application. By delving into pinout configurations, the reader can gain a clear understanding of how to properly connect and use transistors in electronic circuits. Discussion of equivalent alternatives expands the range of options available to users, allowing the flexibility to select compatible alternatives when necessary.
MJ3001 Transistor Pinout
In the TO-3 package, the transistor has three pins: Base, Collector, and Emitter. The pinout arrangement is crucial for correct connections in electronic circuits. Here’s a brief description of each pin:
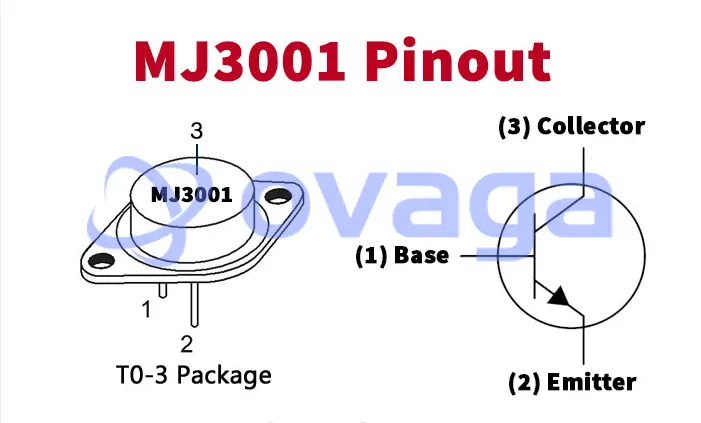
Base (B): The Base pin is responsible for controlling the transistor’s operation. It is used to apply the input signal or bias voltage to the transistor for amplification or switching purposes.
Collector (C): The Collector pin is the main current-carrying terminal of the transistor. It connects to the positive supply voltage or load in typical circuit configurations.
Emitter (E): The Emitter pin is connected to the ground or the negative side of the circuit. It allows the flow of current from the Collector to the Emitter when the transistor is in active mode.
Proper identification and connection of the pins are essential to ensure correct functioning of the MJ3001 transistor in electronic circuits.
MJ3001 Transistor Specs
The following are the specifications of the MJ3001 transistor:
1. Transistor Type: NPN (Negative-Positive-Negative)2. Maximum Collector Current (IC): 10 Amperes3. Maximum Collector-Base Voltage (VCBO): 80 Volts4. Maximum Collector-Emitter Voltage (VCEO): 80 Volts5. Maximum Emitter-Base Voltage (VEBO): 5 Volts6. Maximum Power Dissipation (Pd): 150 Watts7. Transition Frequency (ft): 2 MHz8. DC Current Gain (hFE): Typically 20 to 709. Package Type: TO-3 (Through-Hole Metal Can)
These specifications provide essential information about the electrical and thermal characteristics of the MJ3001 transistor. They help in understanding its performance limitations and selecting appropriate operating conditions for specific applications.